Currently Empty: $0.00
Introducing Artificial Intelligence : Everything You Need To Know

Introduction:
In the world of technology, one concept stands out as a beacon of innovation and transformation: artificial intelligence. From science fiction dreams to real-world applications, AI has captivated humanity’s imagination and transformed the landscape of industries around the world. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamentals of artificial intelligence, uncovering its working and career possibilities.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a fascinating field that delves into the creation and analysis of computational agents capable of acting intelligently. Let’s break down this definition and explore each component:
- Agent: An agent is anything that acts in an environment, ranging from simple entities like worms and thermostats to complex systems like humans and companies. What’s important about agents is their actions and how they behave in various circumstances.
- Intelligent Action: An agent is considered to act intelligently when its actions are appropriate for its goals and circumstances, it can adapt to changing environments and goals, it learns from experience, and it makes suitable choices given its limitations. These limitations include not being able to observe the world directly, having finite memory, and limited time to act.
- Computational Agent: A computational agent is one whose actions can be explained in terms of computation. Whether it’s carried out in human “wetware” or computer “hardware,” the decision-making process of an agent can be broken down into primitive operations that can be implemented in a physical device.
The primary scientific goal of AI is to understand the principles underlying intelligent behavior in natural or artificial systems. This involves analyzing natural and artificial agents, formulating and testing hypotheses about what it takes to construct intelligent agents, and designing, building, and experimenting with computational systems to perform tasks that are typically associated with intelligence.
As part of the scientific process, researchers create empirical systems to test hypotheses and explore possibilities. These systems are distinct from applications built for specific domains.
It’s important to note that the focus of AI is not on intelligent thought itself but rather on how intelligent behavior leads to improved performance. The ultimate engineering goal of AI is to design and synthesize useful, intelligent artifacts that can perform tasks effectively in various applications.
When was Artificial Intelligence invented?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has a rich and fascinating history that dates back to the mid-20th century. The concept of machines exhibiting intelligence and the ability to think for themselves captivated the minds of scientists and researchers, leading to significant breakthroughs in computer science and cognitive studies. Let’s delve into the timeline of AI’s inception and development:
- Alan Turing’s Work at Bletchley Park (1940s): During the Second World War, Alan Turing made groundbreaking contributions to code-breaking efforts at Bletchley Park, UK. His work laid the foundation for modern computer science and introduced fundamental concepts that would later influence the field of AI.
- Turing’s Question of Machine Intelligence (1950s): In the 1950s, Alan Turing posed the question: “Can machines think?” This inquiry sparked a wave of research and exploration into the possibilities of artificial intelligence. Turing’s seminal paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” challenged the notion of human-like intelligence in machines.
- Emergence of Computer and Cognitive Scientists (1950s): Prominent figures in computer science and cognitive studies, such as Marvin Minsky and John McCarthy, recognized the potential of AI in problem-solving and decision-making. Their research, building upon Turing’s work, propelled the field of AI forward and laid the groundwork for future advancements.
- Dartmouth Conference (1956): In 1956, a landmark workshop on artificial intelligence was held at Dartmouth College, USA. Organized by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, this conference is considered the birth of AI as a field of study. Attendees discussed the possibilities of creating machines that could think, understand, learn, and solve problems autonomously.
- Turing Test and AI Development (1950s-present): Alan Turing’s eponymous Turing Test, which evaluates a machine’s ability to exhibit human-like intelligence, remains a cornerstone of AI research. Over the decades, researchers have continued to push the boundaries of AI development, striving to create increasingly sophisticated systems capable of reasoning, learning, and adapting to complex tasks.
Today, AI has invaded almost every facet of modern life, from virtual assistants and autonomous vehicles to medical diagnostics and financial analysis. As technology advances, the search for artificial intelligence continues, with scholars and innovators pushing the boundaries of what intelligent machines are capable of doing. Turing’s and other pioneers’ legacies continue on in the constant goal of developing intelligent systems that rival—and possibly surpass—the capabilities of the human brain.
How does Artificial Intelligence work?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a broad and complex field that encompasses a diverse range of technologies and approaches. At its core, AI seeks to mimic human intelligence and cognitive abilities using computer systems. While there are various techniques and methods employed in AI, the following are some of the fundamental principles that underpin how artificial intelligence works:
- Data Collection and Processing: AI systems rely on vast amounts of data to learn and make decisions. This data can include text, images, videos, sensor readings, and more. The first step in AI involves collecting and preprocessing this data to make it suitable for analysis.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on building algorithms and models that can learn from data. These algorithms analyze patterns and relationships within the data to identify trends and make predictions. There are several types of machine learning approaches, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Supervised Learning: In supervised learning, the algorithm is trained on labeled data, where each input is associated with a corresponding output. The algorithm learns to map inputs to outputs based on the provided examples.
- Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning involves training the algorithm on unlabeled data. The algorithm must find patterns and structure within the data without explicit guidance.
- Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a trial-and-error approach where the algorithm learns by interacting with an environment. It receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties based on its actions and adjusts its behavior to maximize rewards over time.
- Neural Networks: Neural networks are a fundamental building block of many AI systems, particularly in deep learning. These networks are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain and consist of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized into layers. Each layer performs specific computations, and information is passed through the network via weighted connections.
- Input Layer: Receives input data.
- Hidden Layers: Perform computations and extract features from the input data.
- Output Layer: Produces the final output or prediction.
During the training process, the weights of the connections between neurons are adjusted iteratively to minimize the difference between the predicted output and the actual output.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Computer Vision: Natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision are subfields of AI that focus on understanding and processing human language and visual information, respectively. NLP techniques enable AI systems to analyze and generate text, understand speech, and extract meaning from language. Computer vision algorithms allow AI systems to interpret and analyze visual data, such as images and videos, enabling tasks like object recognition, image classification, and facial recognition.
- Decision Making and Problem Solving: Once trained, AI systems can make decisions and solve problems autonomously based on the patterns and knowledge they have learned from the data. These systems can be deployed in various applications, including recommendation systems, autonomous vehicles, medical diagnosis, financial analysis, and more.
Artificial Intelligence career prospects
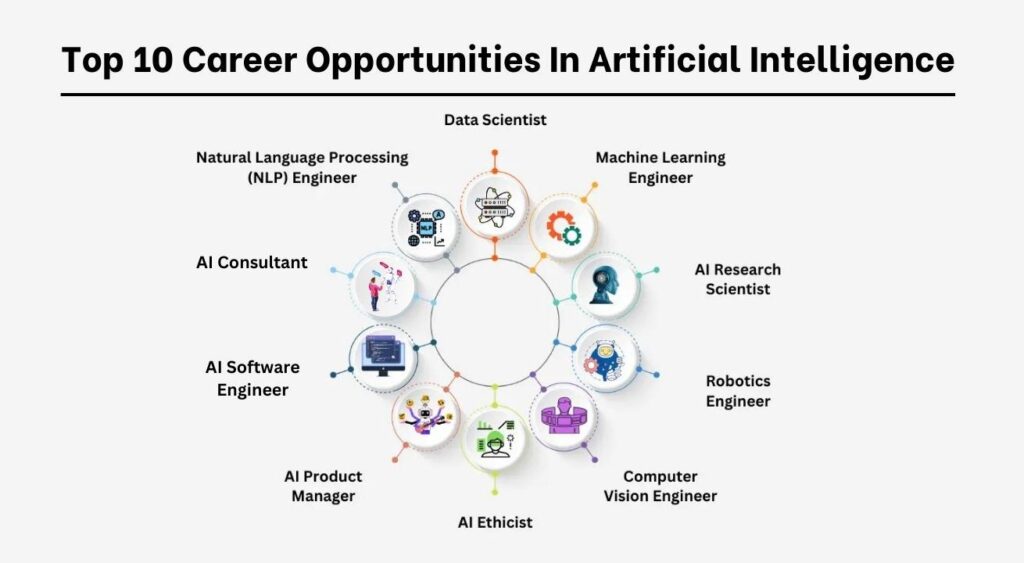
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries across the globe, creating a high demand for skilled professionals in this field. As AI technologies continue to advance and integrate into various sectors, the career prospects for individuals with expertise in AI are exceptionally promising. Let’s explore some of the key career prospects in artificial intelligence:
- Machine Learning Engineer: Machine learning engineers design, develop, and deploy machine learning models and algorithms to solve complex problems. They work closely with data scientists and software engineers to build AI-powered applications and systems.
- Data Scientist: Data scientists analyze large volumes of data to extract valuable insights and patterns using statistical techniques and machine learning algorithms. They play a critical role in developing AI models and leveraging data-driven decision-making in various industries.
- AI Research Scientist: AI research scientists conduct cutting-edge research in artificial intelligence, exploring new algorithms, techniques, and methodologies to advance the field. They work in academia, research institutions, and industry to push the boundaries of AI innovation.
- AI Software Engineer: AI software engineers design and develop software systems and applications that incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. They specialize in implementing AI algorithms, optimizing performance, and ensuring scalability and reliability.
- Robotics Engineer: Robotics engineers design, build, and program robots with AI capabilities to perform tasks autonomously. They work in diverse industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, and aerospace, developing robotic systems for automation and intelligent control.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Engineer: NLP engineers specialize in developing algorithms and systems that enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language. They work on applications such as chatbots, language translation, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition.
- Computer Vision Engineer: Computer vision engineers focus on developing algorithms and systems that enable computers to interpret and analyze visual information from images and videos. They work on applications such as object detection, image classification, and facial recognition.
- AI Ethicist: AI ethicists are responsible for addressing ethical and societal implications associated with AI technologies. They ensure that AI systems are developed and deployed responsibly, considering factors such as bias, fairness, transparency, and accountability.
- AI Product Manager: AI product managers oversee the development and implementation of AI-powered products and solutions. They collaborate with cross-functional teams to define product requirements, prioritize features, and ensure alignment with business goals and user needs.
- AI Consultant: AI consultants provide strategic guidance and advisory services to organizations seeking to adopt AI technologies. They assess business requirements, identify AI opportunities, and recommend tailored solutions to drive innovation and competitive advantage.
Conclusion:
Artificial intelligence (AI) represents a transformative force in technology, shaping the way we interact with machines and revolutionizing industries worldwide. AI, as the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, encompasses various techniques and approaches aimed at replicating cognitive functions typically associated with humans. From learning and reasoning to problem-solving and interacting with the environment, AI systems leverage advanced algorithms, vast datasets, and computational power to achieve intelligent behavior.
The inception of artificial intelligence can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with pioneers such as Alan Turing laying the groundwork for AI research. Over the decades, significant advancements in computer science, cognitive studies, and machine learning have propelled the field forward, leading to breakthroughs in AI development and applications. From the Dartmouth Conference in 1956 to the present day, AI has evolved from theoretical concepts to practical implementations across various domains.
Understanding how artificial intelligence works involves delving into its underlying principles, including data collection and processing, machine learning algorithms, neural networks, natural language processing, and computer vision. These technologies enable AI systems to analyze data, recognize patterns, make decisions, and solve complex problems autonomously. From recommendation systems and virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles and medical diagnosis, AI has become pervasive in modern life, driving innovation and transforming industries.
In terms of career prospects, artificial intelligence offers a plethora of opportunities for individuals with expertise in AI technologies. Roles such as machine learning engineer, data scientist, AI research scientist, and robotics engineer are in high demand, reflecting the growing importance of AI across various sectors. Additionally, specialized roles such as AI ethicist, AI product manager, and AI consultant play crucial roles in ensuring responsible AI development and deployment.
As AI technologies continue to advance and integrate into society, the future of artificial intelligence holds immense promise for addressing complex challenges and driving positive change. Whether it’s improving healthcare outcomes, enhancing productivity in business, or enabling innovative solutions to global problems, artificial intelligence is poised to shape the future of humanity in profound ways. With continued research, innovation, and ethical consideration, AI has the potential to unlock new possibilities and empower us to create a better world.







